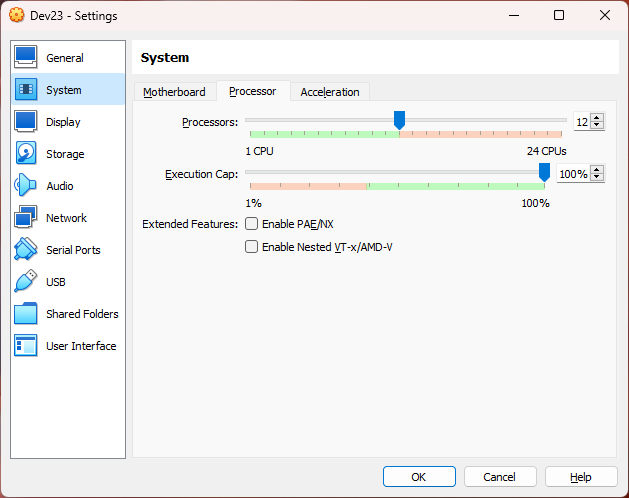
sudo apt update -y && sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo adduser myuser
Note the password you used for defining myuser user
Give myuser 'sudo' permissions
Add the below line right after the line with 'root' definitions
Add 'myuser' as a tty user so it can run 'screen' with no issues:
Modify
to look
myuser
Create folder for myuser software & logs
Allow user 'myuser' to remotly access the AMI via SSH
Export public key from a key-pair:
On Windows:
Open PuttyGen -> Conversions ->Import Key and import your ".pem" file. Right-click in the UI field labeled "Public key for pasting..." -> Select All ->Copy
On MAC/Linux use command:
Note: the file should start from ssh-rsa and should end with imported-openssh-key
Paste content (public key) into vi editor, save and close the file.
Extend the user limit: add the below two lines
myuser hard nofile 500000 myuser soft nofile 500000
to sudo vi /etc/security/limits.conf
Check that you can SSH to the instance with your new user myuser.
Next, reboot and remove the original user - either 'ubuntu' or 'ec2-user'
Optional:
Add a cron job to clean up any our log file older than 14 days
if asked to select an editor for crontab select option '3' - vi.
Add to the crontab file
save file and exit the editor.